Available Technologies
# of Displayed Technologies: 20 / 40
Applied Category Filter (Click To Remove): Technology Types
Categories
 Methods for Anticipating Antibiotic Sensitivity in Bacteria Released from Biofilm Residence
Methods for Anticipating Antibiotic Sensitivity in Bacteria Released from Biofilm Residence
TS-002176 — In order to effectively treat bacterial infections, a clear understanding of the bacterium’s antibiotic sensitivity is needed. Researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital’s Center for Microbial Pathogenesis created a new method to assist in prescribing antibiotics for infections caused by a biofilm to reduce the dosage and the length of antibiotic treatments.
Depending on the bacteria’s physiologic state the antibiotic sensitivity can be highly variable. Originally, bacteria were believed to exist in two physiologic states: planktonic and biofilm. However, the research team based their methods on two additional but transient physiologic states they…
- College:
- Inventors: Bakaletz, Lauren; Goodman, Steven
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Neuregulin-1 as Protection from Respiratory Viral Infections
Neuregulin-1 as Protection from Respiratory Viral Infections
TS-002168 — Children have a higher chance of morbidity and mortality from respiratory viral infections. Severe respiratory viral infections like Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Parainfluenza viruses can lead to the development of asthma in patients. Clinical researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital found that neuregulin-1 (Nrg-1) may be an effective and protective treatment for patients diagnosed with severe respiratory viral infections. Their successful models with mice showed that Nrg-1 may prevent post-viral airway disease and reduce mortality if further studied and applied to human patients in the future.
- College:
- Inventors: Grayson, Mitchell; Hussain, Rehan
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Second Generation Closed Seeding System for the Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft
Second Generation Closed Seeding System for the Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft
TS-001227 — A team of physicians at Nationwide Children's Hospital have developed a process to improve the acceptance of implanted vascular grafts. This Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft (TEVG) is patient-specific. It seeds patient cells onto a biodegradable tubilar scaffold, which is designed to dissolve with hydrolysis so that only the growing vessel remains. This system, the Closed Seeding System, combines patient imaging data, 3D-printing capabilities, and efficient collection and subsequent seeding of patient cells onto the TEVG scaffolding.
- College:
- Inventors: Breuer, Christopher; Hibino, Narutoshi
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Sweat Technology for Monitoring Cystic Fibrosis Health and Adherence
Sweat Technology for Monitoring Cystic Fibrosis Health and Adherence
TS-001225 — Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disorder that affects cells that produce sweat and mucus, causing significant damage to the digestive system, lungs, and other organs. A team at Nationwide Children's Hospital has developed a non-invasive monitoring system to track and test a patient with this disease. This technology is a skin patch that measures the metabolomics of the patients sweat to evaluate the clinical health of patients afflicted with cystic fibrosis.
- College:
- Inventors: Hayes, Don; Kopp, Benjamin; Woodley, Frederick
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Preference Cards and Decision Aid to Facilitate Shared Decision Making in Contraceptive Counseling
Preference Cards and Decision Aid to Facilitate Shared Decision Making in Contraceptive Counseling
TS-001224 — Decks of cards have been used to facilitate knowledge for decades. A team of researchers led by Dr. Elise Berlan have developed a series of cards that combine summaries of contraceptive counciling information and patient preferences. This includes key components of contraceptive preferences which can then be used with a care provider to determine the best form of contraceptive for the patient's preference and decreases the stigma associated with discussing topics like contraceptives as adolecents or young adults.
- College:
- Inventors: Berlan, Elise
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
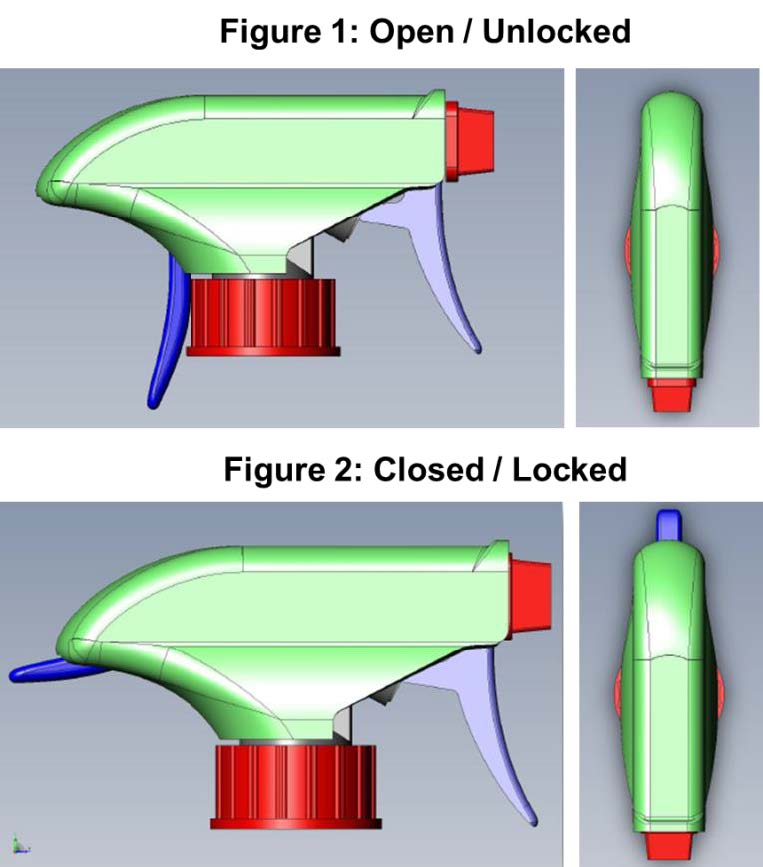 Child-Restraint Spray-Bottle for Household Cleaning Products
Child-Restraint Spray-Bottle for Household Cleaning Products
TS-001037 — When it comes to the safety of our children, innovation never stops. There have been many improvements to the safety of devices and receptacles that can be toxic or life threatening if consumed or exposed to skin. A team of researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have incorporated this desire for security into a common household product: the spray bottle. Often filled with harmful chemicals, spray bottles remain one of the leading causes of chemical exposure injuries in children. The team at NCH has developed a “two-step authentication” spray nozzle that requires the dexterity beyond that of a small child. This dual trigger approach requires a full grip that prevents kids from accessing the contents of the spray bottle, while remaining easily usable by adults and seniors.
Benefits and Applications:
Inventors anticipate that incorporating this product into households will result in a decline in child injury due to accidental activation of spray bottles.
Stage of Development:
- College:
- Inventors: McKenzie, Lara; Nelson, Nicolas; Roberts, Kristin
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 A Virtual Reality Simulation to Aid in Exposure to Therapy for School Avoidance
A Virtual Reality Simulation to Aid in Exposure to Therapy for School Avoidance
TS-001036 — School can be a daunting experience. Constant motion, public speaking and a new environment can increase anxiety in children, sometimes leading to school avoidance. A team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital has developed a solution, where exposure therapy procedures are combined with modern technology can improve the school experience for people of all ages. Using a Virtual Reality (VR) Simulation, clinicians are able to use the multi-user capability to interact with and guide their patient through new environments such as classrooms, hallways and lunchrooms, as well as scenarios known to trigger increased anxiety such as public speaking or asking for help. Biofeedback components help collect data so that the clinician can adapt the experience to the user. Although targeted for school-aged children, this technology can be modified to treat any person with school or public phobia.
- College:
- Inventors: Huang, Yungui; DeForte, Shelly; Luna, John "John"; Mackner, Laura ; Vickery, Elizabeth
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 RyaBhata: A Shiny R Application for Single Cell Transcriptome Data Analysis and Visualization
RyaBhata: A Shiny R Application for Single Cell Transcriptome Data Analysis and Visualization
TS-001035 — Shiny R is an open source platform that allows a framework to develop online applications. With minimal required background in coding principles, a team of researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital were able to display and interact with the analysis made of single-cell transcriptome. Shiny R generates visualizations that include UMAP plots and presents features of single-cell RNA and transcriptomic data without extensive training in R programming. Improvements made on this existing technology includes importing data, cell filtration, principle component analysis, clustering, dimensional reduction, merging datasets, and Graphical user interface (GUI)-based generations of gene expression plots. This significantly improves the visualization and analysis of single-cell transcriptome analysis.
- College:
- Inventors: Manivannan, Sathiyanarayanan ; Garg, Vidu
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Small Molecules that Inhibit and Disperse Salmonella Biofilms in vitro and are Active in Combination with Ciprofloxacin in vivo
Small Molecules that Inhibit and Disperse Salmonella Biofilms in vitro and are Active in Combination with Ciprofloxacin in vivo
TS-001034 — Salmonella is often caused by contact with animals that carry bacteria, contaminated food, or water. It has been observed that children are commonly afflicted by salmonella, and typically treatment includes fluids, medical care, and sometimes pharmaceuticals. A team of researchers at Nationwide Children’s hospital have identified a lead compound that includes a biofilm with anti-salmonella characteristics and acts as an inhibitor. Use of this compound with the antibiotic ciprofloxacin improves the elimination of bacterial infection in at-risk organs such as the liver and spleen.
- College:
- Inventors: Gunn, John; Sandala, Jenna
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Automated Processing of Venous Intravascular Ultrasound Image
Automated Processing of Venous Intravascular Ultrasound Image
TS-001033 — Intravascular Ultrasound Images (IVUS) is a process that uses micro technology to provide images of blood vessels, their inner walls (endothelium) and the inside of veins. The analysis of these images allows clinicians to analyze luminal and scaffold boundaries, identify the presence of stenosis, and perform computations of various geometric quantities. This process is fully automated and therefore eliminates inconsistencies and inefficiencies that are a direct result of current semi-automated or complex fully automated systems already in place.
- College:
- Inventors: Ulziibayar, Anudari
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Use of Tamoxifen to Reduce Breast Implant Capsule Formation and Capsular Contracture
Use of Tamoxifen to Reduce Breast Implant Capsule Formation and Capsular Contracture
TS-001029 — A major complication associated with breast implant prostheses is the occurrence of capsular contracture, occurring in 20%-25% of patients. Severe forms of capsular contracture constitute failure of the reconstruction with significant implications for increased cost owing to an increased need for recurrent medical interventions, as well diminished quality of life for patients. Capsular contracture occurs as the result of the patient’s immunologic ‘foreign body’ response to the implant material. The inventors’ vision is to develop a technology whereby the active metabolites of Tamoxifen (endoxifen) are conjugated to implant biomaterial in a manner allowing for localized delivery of endoxifen. They anticipate that local delivery of endoxifen will successfully reduce capsule formation around implant material by reducing the immunologic foreign body response. This is a technology that could be licensed to implant manufacturers (breast, implantable cardiac devices, etc.)
Technology Overview:
Breast augmentation and reconstruction is a common practice, especially in those afflicted by breast cancer. One of the most common issues that comes with this process is the formation of capsular contracture. This is a direct result of the patient’s immunologic ‘foreign body’ response to the implant material, which can impact the need for significant medical interventions and diminished quality of life. The current pharmacologic treatment for breast cancer is the chemical compound known as Tamoxifen, which acts as a chemo-preventative medication for hormone sensitive breast cancers. A team of researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and Ohio State University aims to localize the delivery of tamoxifen to significantly reduce the immunologic foreign body response around implant material for use in both cancer-based breast reconstruction and cosmetic procedures
Benefits:
No pharmacotherapeutics currently exist to address capsular contracture and no biomaterial advances have been made to specifically reduce the foreign body response to breast implants
Stage of Development:
Mouse studies are currently underway using systemic delivery of Tamoxifen for treatment of capsular contracture in breast implants. A manuscript is in preparation.
Future mouse studies will focus on local delivery of endoxifen for treatment of capsular contracture in breast implants; then look at other implant types and different coating types.
Potential Applications / Markets:
According to the report published by Allied Market Research, the medical implant industry estimated $85.38 billion in 2019, and is estimated to generate $147.46 billion by 2027, manifesting a CAGR of 7.2% from 2020 to 2027. According to a report published by Fortune Business Insights, the breast implant market was worth $2.76 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $3.05 billion by the end of 2027, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period, 2020-2027.
Opportunity / Seeking:
-Licensing
IP Status:
Patent application submitted
- College:
- Inventors: Blum, Kevin
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
.png) Virtual Reality-Based Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury Assessment and Rehabilitation Platforms
Virtual Reality-Based Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury Assessment and Rehabilitation Platforms
TS-000621 — Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of acquired disability in U.S. children and adolescents. Impairment of executive functions post-TBI has broad and profound implications for everyday life of pediatric patients, and the development of effective rehabilitation strategies is of significant clinical importance. Researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have developed virtual reality (VR)-based programs for assessing cognitive function and providing subsequent rehabilitation. This pediatric TBI assessment software provides VR-based cognitive-assessment tasks and an additional training platform that pairs with the Oculus Rift virtual reality viewer. The training program is designed with a series of environmentally-enriched three-dimensional cognitive exercises that aid in rehabilitation of executive core functions among pediatric patients with TBI in a highly controlled, safe, and automated manner.
- College:
- Inventors: Xiang, Henry; Patterson, Jeremy; Shen, Jiabin
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
.png) Closed Seeding System for the Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft
Closed Seeding System for the Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft
TS-000620 — Physicians at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have developed a Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft (TEVG) by seeding patient cells onto a biodegradable tubular scaffold. The scaffold degrades by hydrolysis, ultimately leaving only the growing vessel in the patients. The Closed Seeding System enables efficient collection and seeding of patient cells onto the TEVG scaffold, which has been further optimized by using patient imaging data and 3D-printing capabilities to create patient-specific vascular grafts for implantation.
- College:
- Inventors: Breuer, Christopher; Best, Cameron ; Strouse, Robert
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
.png) Closed Seeding System for the Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft
Closed Seeding System for the Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft
TS-000619 — Physicians at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have developed a Tissue Engineered Vascular Graft (TEVG) by seeding patient cells onto a biodegradable tubular scaffold. The scaffold degrades by hydrolysis, ultimately leaving only the growing vessel in the patients. The Closed Seeding System enables efficient collection and seeding of patient cells onto the TEVG scaffold, which has been further optimized by using patient imaging data and 3D-printing capabilities to create patient-specific vascular grafts for implantation.
This is an improvement on an existing product. This second-generation system possesses all of the advantages of the previous system including improved safety, efficacy and simplicity. In addition, it has the potential for further improved efficacy and better efficiency.
Benefits:
Using current methods, few hospitals can perform implantations of tissue engineered vascular grafts. TEVG preparation requires advanced collection methods for the cells to be seeded onto the scaffold of the TEVG and must be performed in a sterile environment. The Closed Seeding System enables surgeons to collect patient cells and prepare the TEVG in a standard surgical setting, greatly expanding the availability of this surgery.
Further Details/Stage of Development:
The Closed Seeding System has been tested in an animal model of TEVG implantation.
Potential Applications/Markets:
Initial application of the technology would be used to seed a biodegradable tubular scaffold with autologous bone marrow derived mononuclear cells while simultaneously re-transfusing the residual bone marrow cells (primarily red blood cells) back to the patient. This technology could be used in any application where a specific component of a patient’s blood or bone marrow is removed and processed and the residual cells are returned to the donor.
Opportunity/Seeking:
Development Partner
Commercial Partner
Licensing
IP Status:
Patent Pending
- College:
- Inventors: Breuer, Christopher; Hibino, Narutoshi
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
.png) Methods of Treating and Preventing Intestinal Injury Related to Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation
Methods of Treating and Preventing Intestinal Injury Related to Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation
TS-000610 — Hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation (HS/R)-induced injuries often result from trauma or severe blood loss and can quickly progress to organ failure. Researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have developed a novel method for treating subjects at risk for HS/R by administering Heparin Binding-Epidermal Growth Factor (HB-EGF). Administration of HB-EGF protects intestinal epithelial and endothelial cells from HS/R-induced injury in a rat model. This novel method may have broad clinical availability for treating or preventing a range of intestinal injuries in pediatric and adult patients.
- College:
- Inventors: Besner, Gail; El-Assal, Osama
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
.png) Neuromuscular GRO worksheet
Neuromuscular GRO worksheet
TS-000596 — Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a severe neuromuscular disease and the leading genetic cause of infant mortality. Moreover, existing treatments suffer from notable floor and ceiling effects and also poorly discriminate improved motor performance in patients. To circumvent these challenges, researchers at Nationwide children’s have developed the Neuromuscular Gross Motor Outcome (GRO) worksheet. The GRO worksheet is a gross motor outcome measure designed to assess whole body strength, motor development and function for all levels of ability across the lifespan in those diagnosed with SMA. Hence, the GRO worksheet is the ideal outcome measure tool for SMA or similar conditions to answer the need to quantity gross motor ability across a wide age span.
- College:
- Inventors: Lowes, Linda; Alfano, Lindsay; Iammarino, Megan; Reash (Miller), Natalie
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Lowes Lab Ambulatory Status Algorithm (LASA)
Lowes Lab Ambulatory Status Algorithm (LASA)
TS-000501 — Research in the field of neuromuscular disease is increasing at an astonishing pace. However, there is no current standardization in the evaluation of the ambulatory status of patients. Researchers at Nationwide Children’s have devised a guide that stratifies patients into ambulatory statuses for data analysis and group assignment. Unlike the traditional binary stratification, this method adds a third stratification which is very important for clinical trial planning and an accurate assessment of the ambulatory status of patients.
- College:
- Inventors: Lowes, Linda; Reash (Miller), Natalie
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Method for Inhibiting the Growth of Intrabacterial Pathogens Salmonella and Francisella in the Infected Cells (KH-2)
Method for Inhibiting the Growth of Intrabacterial Pathogens Salmonella and Francisella in the Infected Cells (KH-2)
TS-000499 — Intrabacterial pathogens are infectious bacteria that infiltrate cells and infect those that come in contact with them. Significant bacterial infections include those of salmonella, often caused by the consumption of contaminated food, and francisella, caused by handling infected animal tissue. A team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital has developed novel therapeutics to inhibit the growth of these bacteria in infected cells, designated as KH-1 and KH-2. These compounds target the host immune pathway to help the infected cell control bacterial growth, and control infections in not only antibiotic susceptible strains, but also multidrug resistance strains.
Benefits:
The proposed application of the compound is a novel method to control infections by intracellular pathogens. Traditional antimicrobials directly target bacteria and frequently select for antibiotic resistant mutants. Our preliminary data indicate that KH-1 does not directly kill bacteria, rather it targets the host immune pathway to help the infected cell control bacterial growth. The KH-1 is proposed for controlling infections by not only antibiotic susceptible strains but also multidrug resistance strains.
Stage of Development:
The use of antimicrobials to treat infections selects for antibiotic resistant mutants. Antibiotic
resistance is a top threat to public's health. In the U.S alone, antibiotic resistance is responsible for more than 2 million infections and 23,000 deaths per year (CDC 2019). Novel intervention strategy is urgently needed to combat multidrug resistant strains and replace the use of antibiotics.
Prototype: Intracellular pathogens use multiple mechanisms to manipulate the host cell immunity in
such a way that is favorable for pathogens to grow and ultimately cause host cell death that is indicated by releasing some intracellular components from the infected host cells including lactate dehydrogenase. Host targeted-drugs protect the infected cell from death can be used as host therapy to control infections-it allows the infected host cell time to kill the ingested microbe. We screened a kinase inhibitor library for compounds that limit cell death from Salmonella infection and identified KH-1 as antiSalmonella, and in subsequent testing, also anti-Francisella.
Proof of principle: KH-1 treatment reduces host cell lysis and intracellular bacterial (Salmonella and Francisella) growth inside J774.1 macrophages. KH-1 also protects the mice from lethal Salmonella and Francisella infection.
Future Work:
1- We will identify KH-1 target(s) in the host cell and investigate how KH-1 helps the infected cell to limit bacterial growth.
2- We will study any observed side effects of KH-1 to the host.
3- We will study pharmacokinetics and dynamics of KH-1.
4- We will improve KH-1 delivery to achieve the best effects.
5- We will examine the effects of KH-1 on controlling multi-drug resistant intracellular bacterial
strains.
Potential Applications / Potential Markets:
1- Treating infection caused by intracellular pathogens not limiting to Salmonella and Francisella.
2- Treating infections caused by multidrug resistant intracellular pathogens.
Opportunity/Seeking:
Commercial Partner
Licensing
IP Status:
Patent Application Submitted
Provisional Patent
- College:
- Inventors: Hoang, Ky; Gunn, John
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Method for Inhibiting the Growth of Intrabacterial Pathogens Salmonella and Francisella in the Infected Cells (KH-1)
Method for Inhibiting the Growth of Intrabacterial Pathogens Salmonella and Francisella in the Infected Cells (KH-1)
TS-000480 — Intrabacterial pathogens are infectious bacteria that infiltrate cells and infect those that come in contact with them. Significant bacterial infections include those of salmonella, often caused by the consumption of contaminated food, and francisella, caused by handling infected animal tissue. A team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital has developed novel therapeutics to inhibit the growth of these bacteria in infected cells, designated as KH-1 and KH-2. These compounds target the host immune pathway to help the infected cell control bacterial growth, and control infections in not only antibiotic susceptible strains, but also multidrug resistance strains.
Benefits:
The proposed application of the compound is a novel method to control infections by intracellular pathogens. Traditional antimicrobials directly target bacteria and frequently select for antibiotic resistant mutants. Our preliminary data indicate that KH-1 does not directly kill bacteria, rather it targets the host immune pathway to help the infected cell control bacterial growth. The KH-1 is proposed for controlling infections by not only antibiotic susceptible strains but also multidrug resistance strains.
Stage of Development:
The use of antimicrobials to treat infections selects for antibiotic resistant mutants. Antibiotic
resistance is a top threat to public's health. In the U.S alone, antibiotic resistance is responsible for more than 2 million infections and 23,000 deaths per year (CDC 2019). Novel intervention strategy is urgently needed to combat multidrug resistant strains and replace the use of antibiotics.
Prototype: Intracellular pathogens use multiple mechanisms to manipulate the host cell immunity in
such a way that is favorable for pathogens to grow and ultimately cause host cell death that is indicated by releasing some intracellular components from the infected host cells including lactate dehydrogenase. Host targeted-drugs protect the infected cell from death can be used as host therapy to control infections-it allows the infected host cell time to kill the ingested microbe. We screened a kinase inhibitor library for compounds that limit cell death from Salmonella infection and identified KH-1 as antiSalmonella, and in subsequent testing, also anti-Francisella.
Proof of principle: KH-1 treatment reduces host cell lysis and intracellular bacterial (Salmonella and Francisella) growth inside J774.1 macrophages. KH-1 also protects the mice from lethal Salmonella and Francisella infection.
Future Work:
1- We will identify KH-1 target(s) in the host cell and investigate how KH-1 helps the infected cell to limit bacterial growth.
2- We will study any observed side effects of KH-1 to the host.
3- We will study pharmacokinetics and dynamics of KH-1.
4- We will improve KH-1 delivery to achieve the best effects.
5- We will examine the effects of KH-1 on controlling multi-drug resistant intracellular bacterial
strains.
Potential Applications / Potential Markets:
1- Treating infection caused by intracellular pathogens not limiting to Salmonella and Francisella.
2- Treating infections caused by multidrug resistant intracellular pathogens.
Opportunity/Seeking:
Commercial Partner
Licensing
IP Status:
Patent Application Submitted
- College:
- Inventors: Hoang, Ky; Gunn, John
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
 Development Using CRISPR/Cas9 of a TTN Based Cardiomyopathy Mouse Model TTN219
Development Using CRISPR/Cas9 of a TTN Based Cardiomyopathy Mouse Model TTN219
TS-000382 — Experts at Nationwide Children's Hospital have developed a novel Titin-deficient mouse, TTN 219, in order to study limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2J (LGMD2J) based on a documented patient mutation. The TTN219 mouse model was developed using CRISPR/Cas9 technology therefore the time required to modify the Titin gene is reduced as well as off-target insertions into the mouse genome. Our experts have demonstrated functional deficits in skeletal muscles of the TTN219 mouse model and plan to use this model to test therapeutic strategies intramuscularly and systemically to restore Titin protein function.
- College:
- Inventors: Rodino-Klapac, Louise ; Potter, Rachael
- Licensing Officer: Murrah, Kyle
